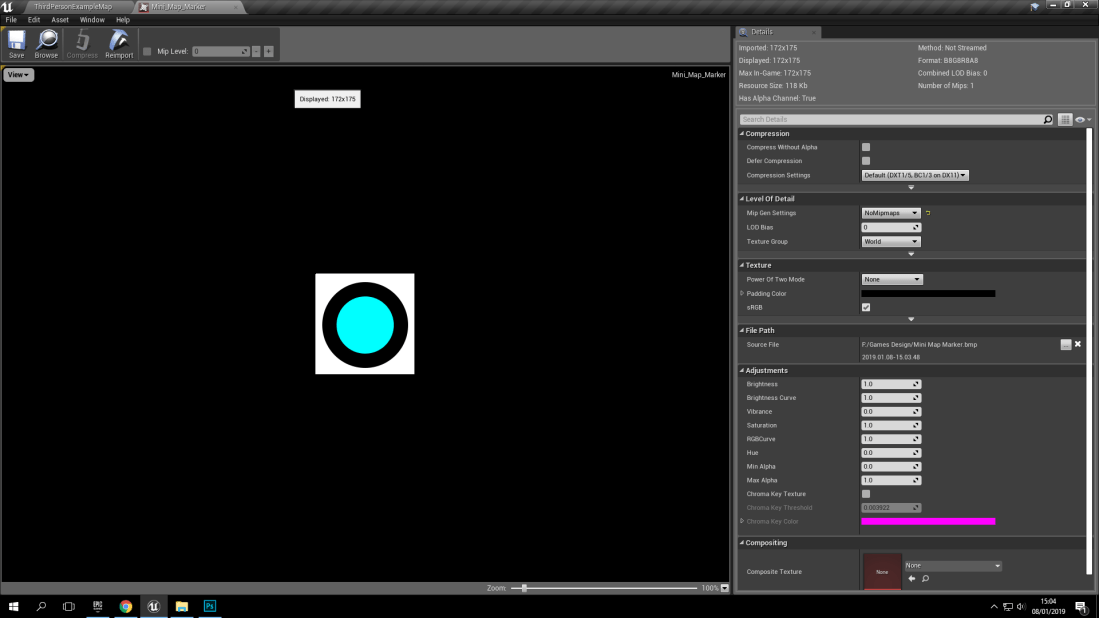
This new project is all about sound! With the sound, I decided to study different types of ambience! (Ambience means the atmosphere and character that the music creates). With the ambience created by a GameCube classic, (Luigi’s Mansion) creates a tense and unsure ambience, Since in the ambience we get to hear Luigi (The protagonist) humming to the tune that we also hear as the player. But if you have played other Mario games, Then you will know the character of the younger brother to the Nintendo hero we all know and love. The reason why I mention this is because Nintendo did this on purpose, To further give the players an uneasy sense of ambience in the sounds and music played because of the character’s vocal lines having the same ambience!

Kirby’s Epic Yarn! A personal favorite game of mine just for the ambience! The reason why this ambience is not only because of the reason above, But instead of Luigi this time it’s Kirby! A pink puffball who’s always cheery and hyperactive! For the actual theme of the ambience it’s very cheery and uplifting, similar to the personality that Kirby is known for. This is also because Nintendo mainly makes child-friendly games that fans are going to remember. This is one of those games that people remember for the amazing music (ambience).
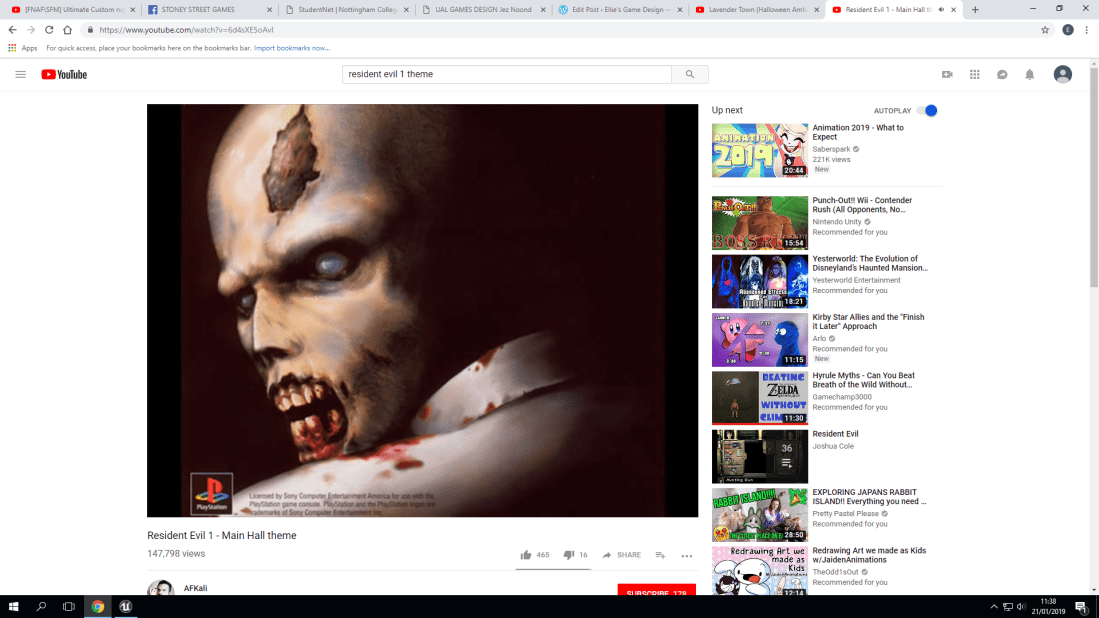
Now we move onto a more classical horror game. Resident Evil 1 (For the playstation. Not the remastered version. This is the original one). With the backstory for this game, You play as two main characters, Jill Valentine and Chris Redfield. In the game, the place that you explore is huge. However, the main hall is a place you will visit frequently. For the ambience of this it makes you very on edge. This could be because you can often find enemies near or in the main hall as you explore. But that also does mean that this ambience can also be described as ominous. You don’t know much about why you’re here or where the other characters are, Which means that this ambience plays perfectly into the story that this game tells.
Part One: 3 Types Of Sound:
The three types of sound that we learned and experimented with are called:
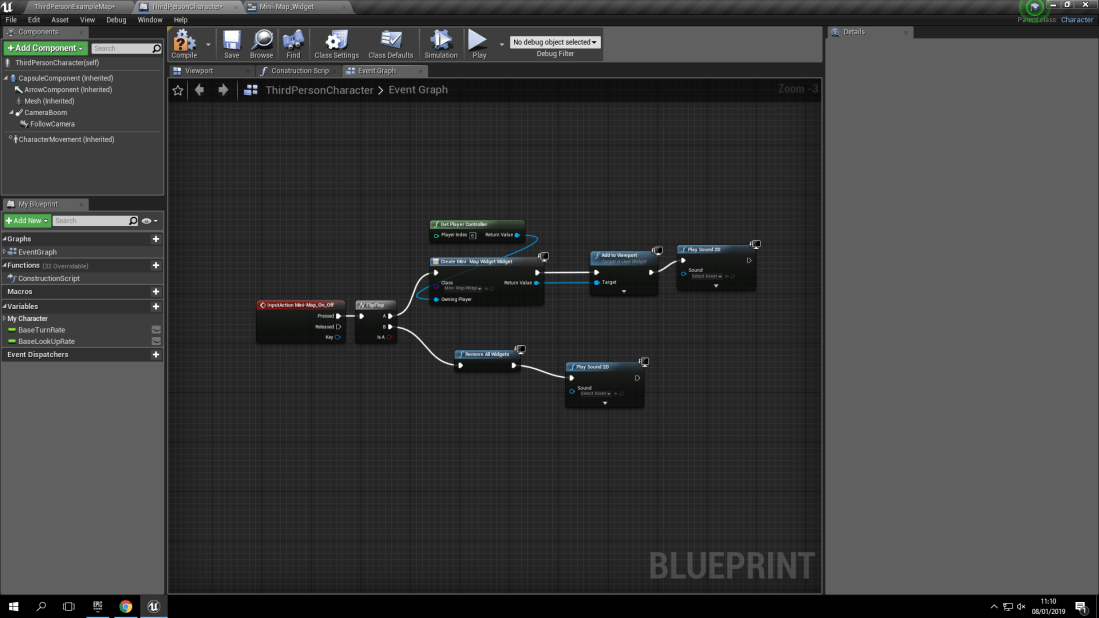
- Play Sound 2D
- Play Sound at location
- Sound Cue with attenuation (Plays sound in the world)
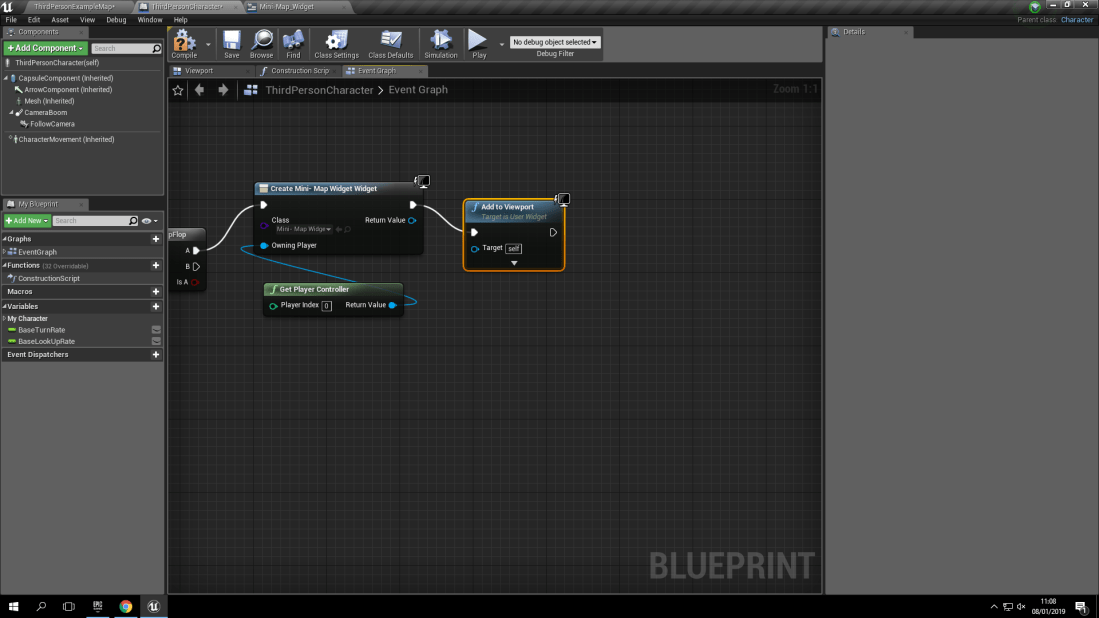
Play Sound 2D: What Does It Mean?:
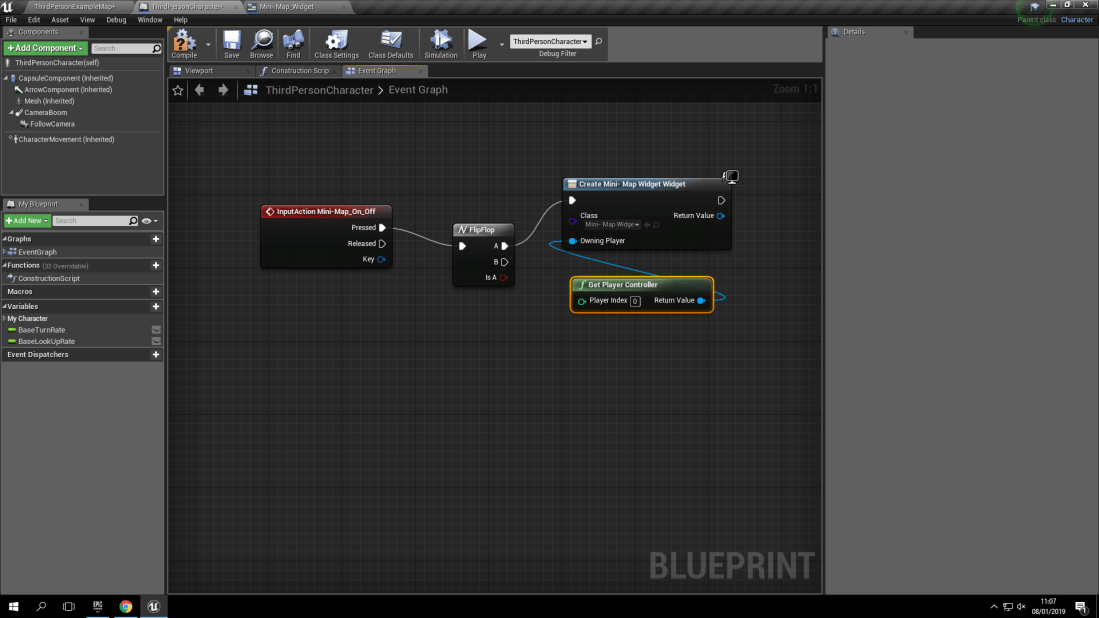
With the type of sound known as ‘Play sound 2D’ it means that the sound will be played in a 2D fashion. What this means is that it will only be heard when the collision box it’s associated with will play the sound. Which is then programmed via a blueprint to play the sound once when the collision box is triggered. For example, In my world, I made a simple cube and added a collision box to it. Then I made a blueprint inside of the collision box (Which is called ‘Box’ to stop any confusion).
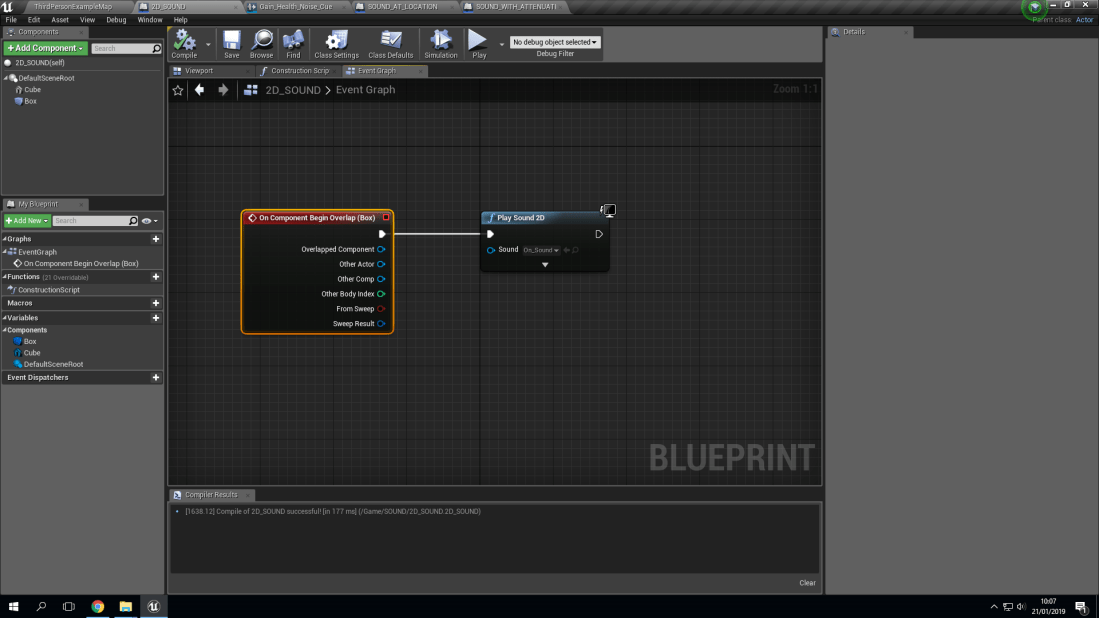
Play Sound At Location: What Does It Mean?:
With playing a sound at a location, what this means is that you are able to program the sound to play at a certain location as long as you program it correctly. For example, if you were to program the sound to play 50 units in the x axis to your player then as soon as they trigger the collision box, the sound will play at the location that you have decided to make the sound play at.
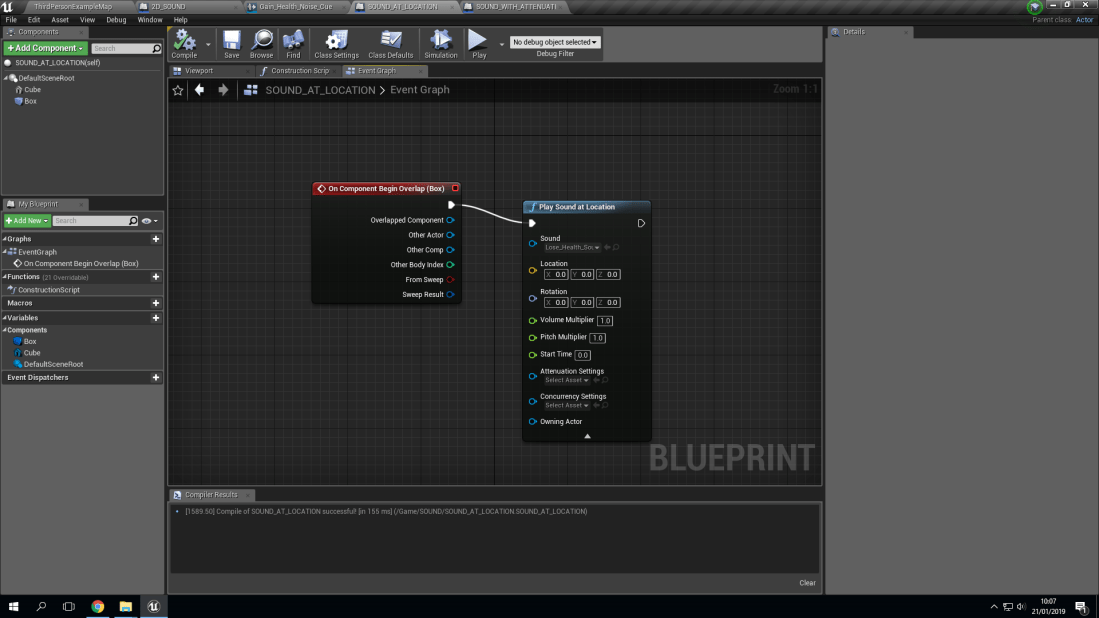
Sound Cue With Attenuation: What Does It Mean?:
Attenuation is known to be defined as the reflection of a sound or an electrical current. To further define this, Attenuation can be described as how you hear sound. The further you are from the source (What is making the sound) the quieter it will be. It can be defined also with terms such as Attenuation is how much distance you have from the epicenter of the source, which means the volume will be higher or lower depending on the distance you have from the source.
Part Two: Violins And Determination:
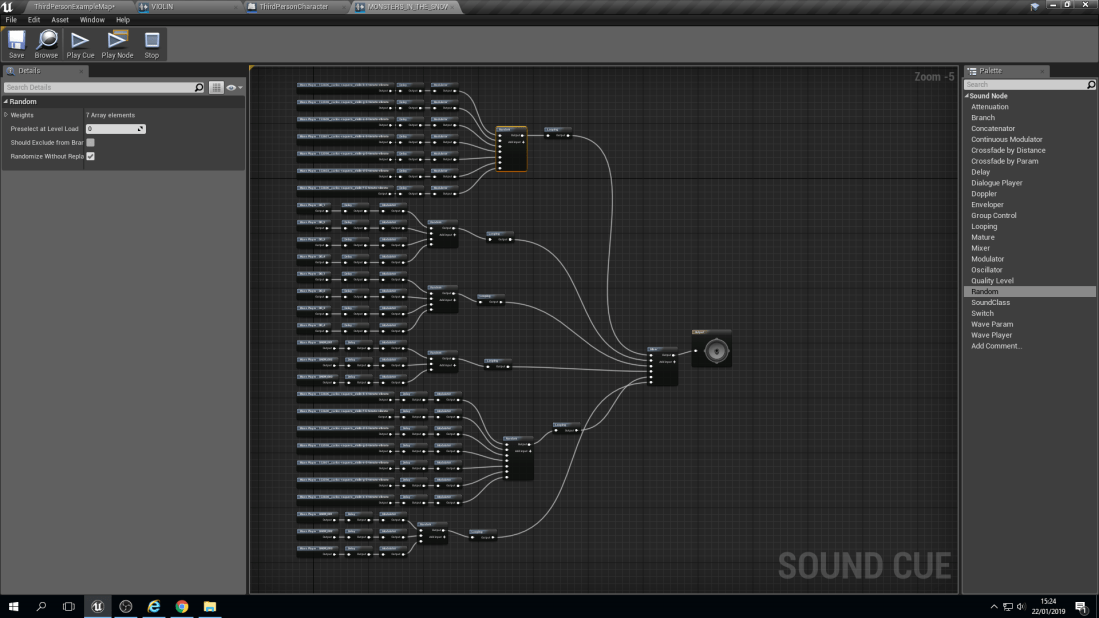
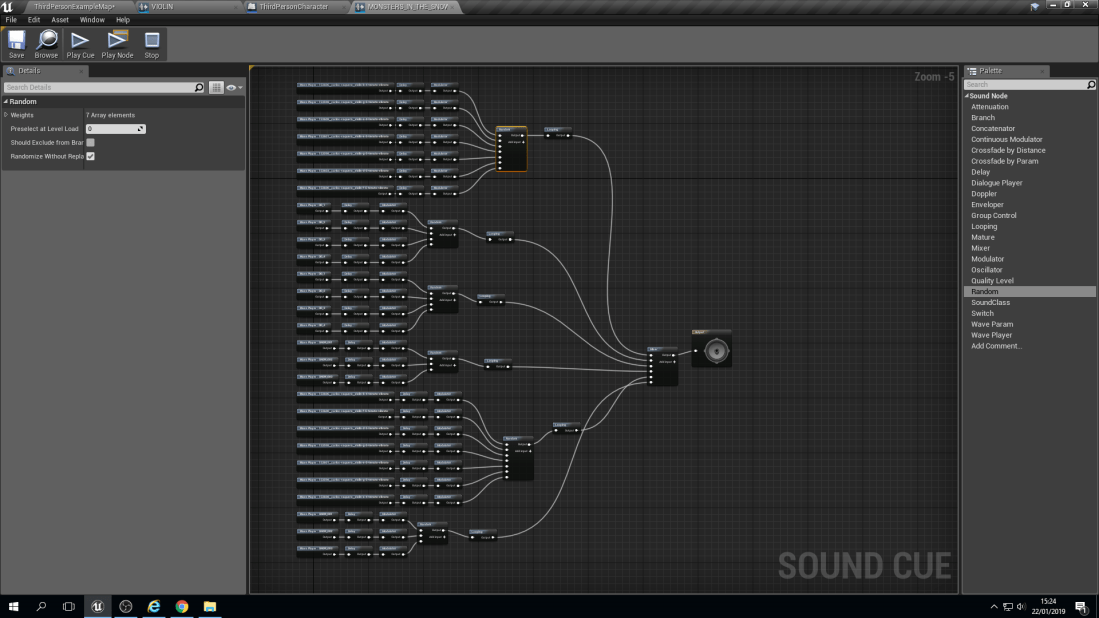
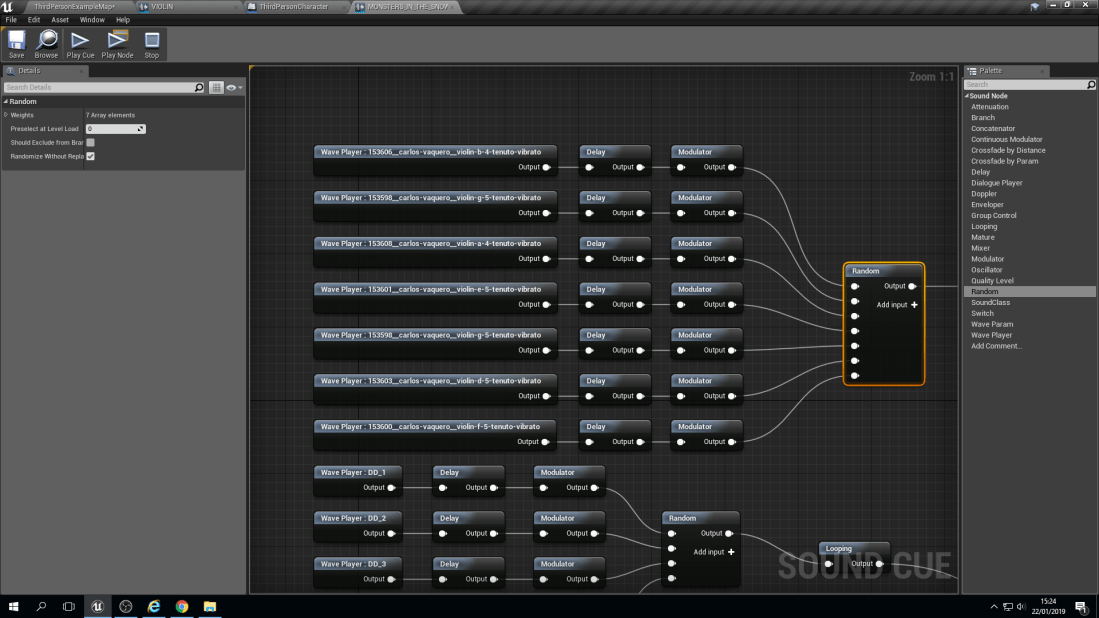
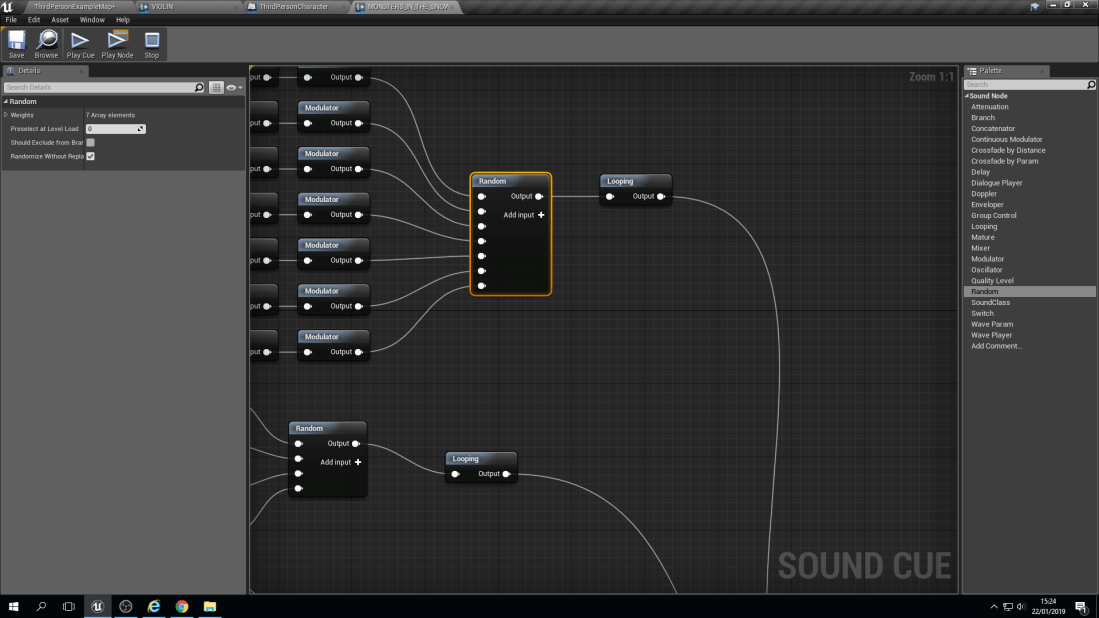
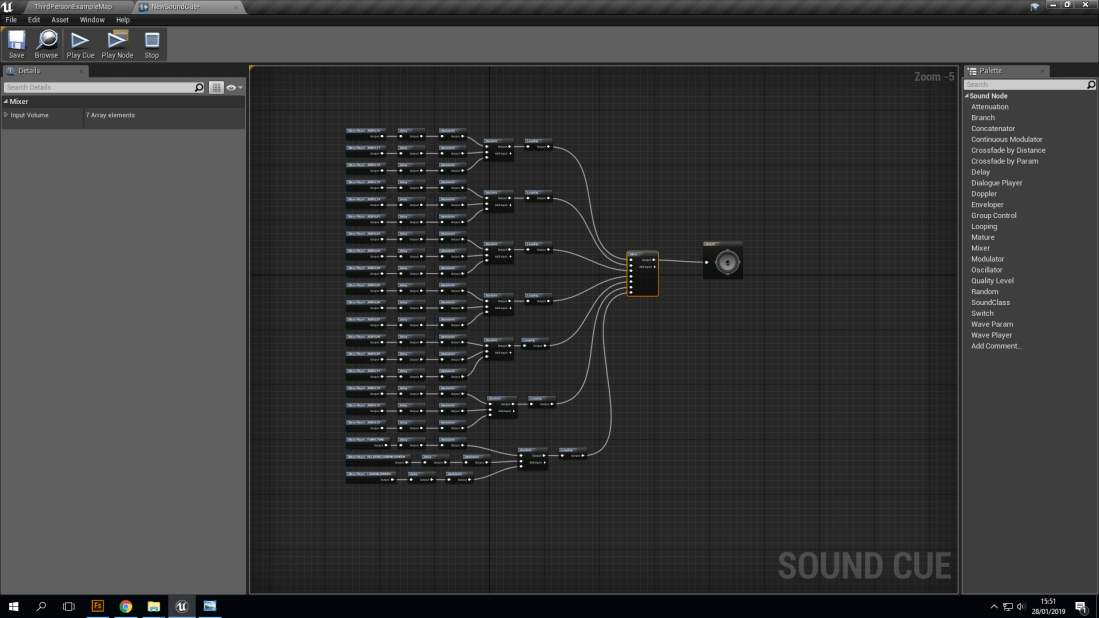
With this blueprint it does look very complex but it’s not. The way that they have been separated is into Chords. A chord is made up of 3 notes on a piano. For example, a ‘C’ chord would be ‘C’, ‘E’ and ‘G’. Then they are all individually linked up to a node known as a ‘Delay’. A delay does as it says in it’s name, It delays the sound from playing from a lowest point of delay to a highest. For example, A ‘G’ note could have a 1 second to 3 seconds delay, meaning it can play anywhere between those two numbers but no lower than 1 second and no longer than 3 seconds.